
04 Sep Thermal Insulation Performance of ACP in Curtain Walls
Table of Contents
ACP panels can help keep heat inside curtain walls, but how well they work depends on a few things. Thermal insulation is important for saving energy and keeping rooms comfortable. In curtain walls, the panel thickness, the core material, and how the panels are put in all change how much heat gets through. For example, panels with vacuum insulation and fumed silica cores let less heat pass than regular materials. How workers handle thermal bridges and pick panel systems also affects how much heat leaves curtain walls. Compared to other cladding materials, ACP is lighter, works well, and lets designers be creative in curtain walls.
Key Takeaways
ACP panels help keep heat inside buildings. They do this by using layers and insulated cores.
Thicker panels and special cores help stop heat from escaping. Sealed joints and air spaces also help save energy.
ACP panels bounce sunlight away. This can lower cooling costs by 30%. It can also lower heating costs by 25%. Buildings feel more comfortable.
ACP panels are lighter than concrete, glass, or stone. They are easier to put in place. They work better to keep heat in and need less care.
Adding thermal breaks and ventilated spaces helps save energy. Extra insulation and good glazing with ACP panels make curtain walls more efficient and green.
ACP and Thermal Insulation
Effectiveness in Curtain Walls
Aluminum Composite Panels are important in curtain wall systems. They have many layers, and the core is often mineral or aluminum honeycomb. This helps stop heat from moving through the building. The layers make curtain walls better at keeping heat out or in. They also help keep indoor temperatures steady. ACP panels send less heat outside than glass sheets. This keeps rooms cooler and lowers the building’s heat load.
In tropical places, studies show ACP on brick walls can make rooms cooler. This makes people inside more comfortable. When ACP and insulation are used together, thermal insulation gets better. The air gap and type of insulation matter a lot. How well ACP works depends on the climate and the wall’s design. In hot places, stone cladding can cool buildings better than ACP. But ACP still gives good thermal efficiency and lasts a long time.
ACP is better than PVC sheets for thermal insulation and lasts longer. This is because it has aluminum and layers. ACP panels with mineral cores, like magnesium oxide or aluminum hydroxide, work even better. They also resist fire. These things make ACP a good choice for curtain walls in homes and offices.
Benefits and Drawbacks
ACP panels have many good points for curtain walls. Their layers slow down heat flow and stop thermal bridging. This is a big reason for heat loss in buildings. Special coatings like PVDF or nano-coatings can reflect up to 70% of sunlight. This helps keep rooms cooler and lowers air conditioning use. Energy use for cooling can drop by 20-30%. Heating needs can go down by 15-25%. ACP panels help keep inside temperatures steady. This makes buildings more comfortable and saves energy.
Note: ACP panels can be used with glass curtain walls. This lets in more daylight. It can cut down on artificial lighting by up to 40%. This saves even more energy.
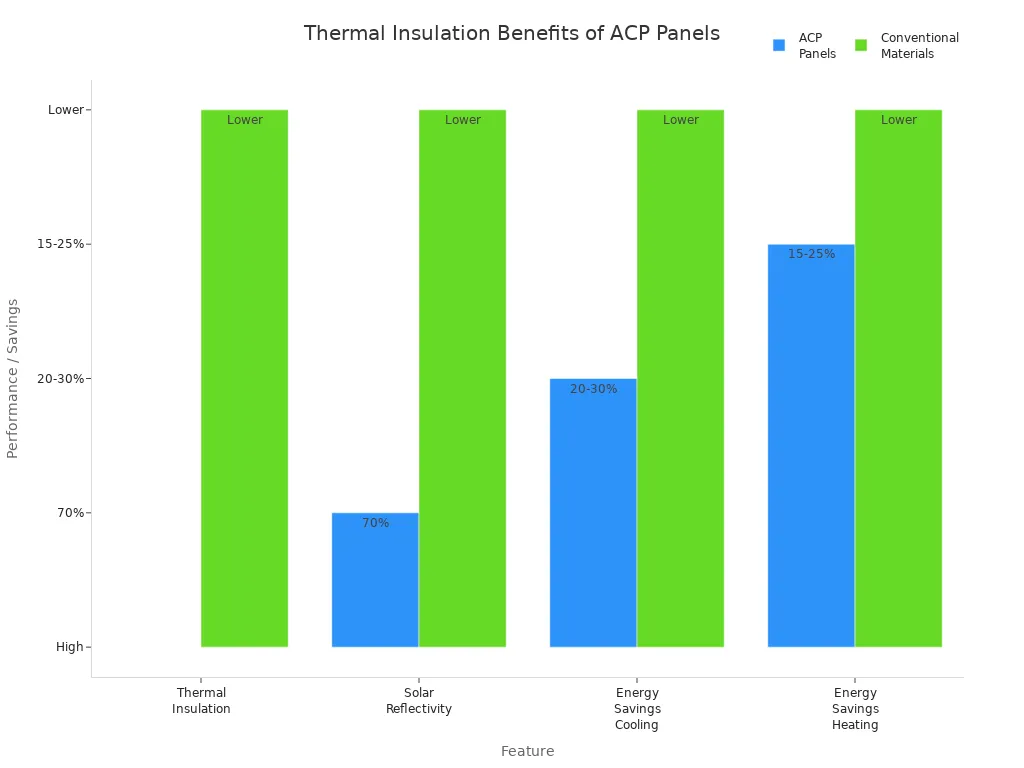
The table below shows how ACP panels compare to other materials:
Feature | Aluminium Composite Panel (ACP) | Conventional Materials (Concrete, Brick, Glass) |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Insulation | High – multi-layered construction reduces heat flow and thermal bridging | Moderate to Low |
Solar Reflectivity | Up to 70% with PVDF or Nano-coatings, reflecting sunlight and reducing heat gain | Lower reflectivity |
Energy Savings in Cooling | 20-30% reduction in cooling energy due to heat regulation and reflectivity | Less efficient |
Energy Savings in Heating | 15-25% reduction by preventing heat loss in winter | Less efficient |
ACP panels do have some downsides. In hot places, stone cladding can cool buildings better than ACP. Using ACP can make outdoor air a little warmer. This can add to the urban heat island effect. Fire risk is also a worry. But using mineral core ACP panels and safe insulation can help with this.
In summary, ACP panels work well in curtain walls. They help with thermal insulation and save energy. They also look good in modern buildings. How well they work depends on the core, thickness, and how they are used with other wall parts.
ACP Structure
Panel Thickness
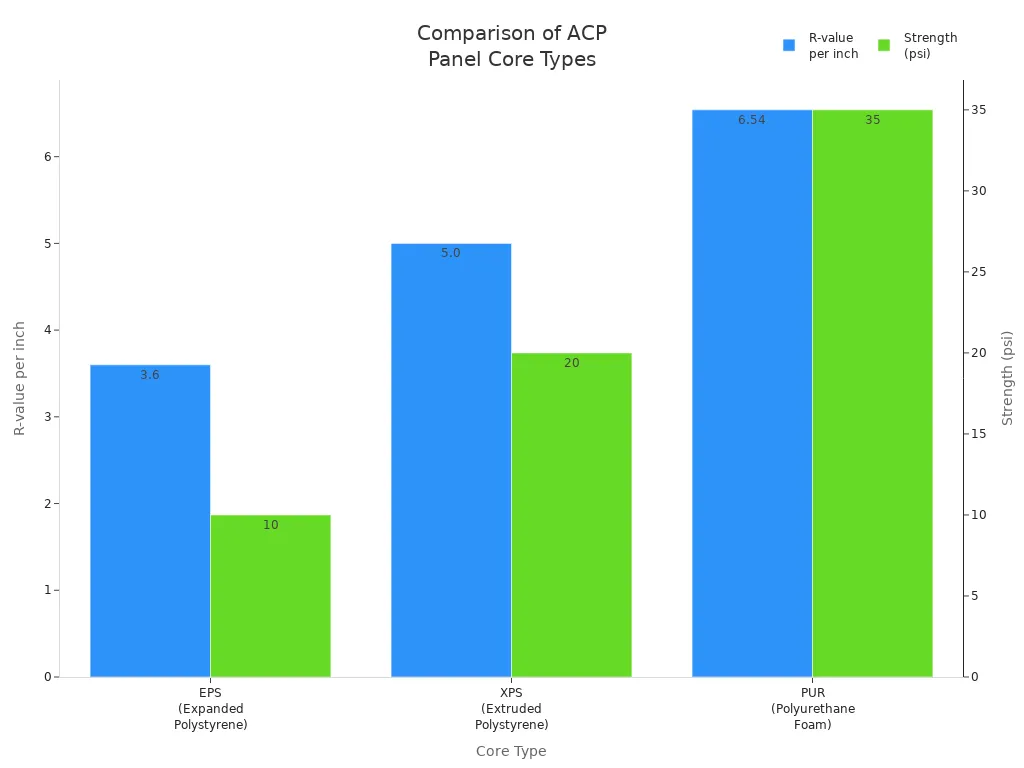
Panel thickness is very important for curtain wall systems. Thicker panels with foam cores stop more heat from moving. Designers can pick foam core thickness from 10mm to 140mm. This gives choices for different insulation needs. Foam core materials like PU, XPS, PET, PVC, and EPS do not let heat pass easily. Their thermal conductivity is about 0.03 W/m·K. This means the panel slows heat transfer and raises the r-value. When the foam core is thicker, it blocks heat even better. Some foam types also keep water out, add strength, and are light. These things make them good for panels that need insulation.
Thicker foam cores block more heat.
Foam core panels can be used in many climates.
Low thermal conductivity helps keep heat in or out.
Core Material
The core material inside the panel changes fire safety and insulation. The table below shows common core types:
Panel Type | Core Material | Thermal and Fire Properties |
|---|---|---|
ACP | Polyethylene (light plastic) | Not as fire safe, less insulation, light, cheaper |
ACM | Mineral-filled (polypropylene) | Better fire safety, more insulation, stronger |
Mineral-filled cores are safer in fires and insulate better. ACP panels with PET foam cores help keep rooms at a steady temperature. They also lower energy use. These foam cores make the panel lighter and quieter. Mineral cores slow down fire and keep the wall strong. Each core type has its own balance of weight, price, and safety.
Air Cavities
Air cavities in curtain walls act as a barrier to the outside. These spaces let air move and help protect the panel layers. They also cut down on heat loss. The air cavity works like a filter and keeps the building safe from outside weather. It also makes the wall better at stopping heat. When you add insulation, air cavities help even more. This keeps rooms comfortable and saves energy.
Tip: Air cavities with insulation can raise the r-value and save more energy in curtain wall systems.
Factors Affecting Thermal Performance
Installation Methods
How ACP panels are installed matters a lot. If workers use insulation all over and seal joints well, less heat gets through. Bad seals or gaps let air leak out. This makes the wall lose more heat. It also lowers the r-value and raises the u-value. Installers use fasteners, glue, or brackets to put up ACP panels. Each way changes how well the wall stops heat. Good insulation behind the panels helps the whole wall work better. When workers do a careful job, buildings stay warmer or cooler. This saves energy.
Tip: Sealing joints and using insulation everywhere helps curtain walls have lower u-values and higher r-values.
Insulation Layers
Adding insulation layers to ACP curtain walls helps keep heat in or out. Designers pick things like mineral wool, foam, or fiberglass. These go behind or between the ACP panels and the building. Thicker insulation makes the r-value go up and the u-value go down. This means the wall works better. Insulation also stops water and moisture from getting in. This keeps the building safe. If you use insulated glass too, the wall works even better and meets energy rules.
A table below shows how different insulation types change r-values and u-values:
Insulation Type | Typical r-value | Typical u-value (W/m²·K) | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Mineral Wool | 3.0 – 4.0 | 0.25 – 0.33 | High |
Rigid Foam | 4.5 – 6.0 | 0.16 – 0.22 | Very High |
Fiberglass | 2.5 – 3.7 | 0.27 – 0.40 | Moderate |
Ventilated Cavities
Ventilated cavities help curtain walls work better. They let air move between the ACP panels and the building. This air space acts like a shield. It slows down heat moving through the wall. It also lowers the u-value. Air in the cavity takes away extra heat in summer. It removes moisture in winter. Designers use ventilated cavities with insulated glass to make the wall work the same everywhere. These cavities also stop water from building up. This keeps the panels and insulation safe. When you add good insulation, ventilated cavities help rooms stay comfortable.
Note: Ventilated cavities work best with sealed joints and insulation everywhere.
Thermal Breaks
Thermal breaks are very important for ACP curtain walls. Makers put plastic, rubber, or polyamide between aluminum parts. This stops heat from moving through the metal. It cuts down on thermal bridging. That means less heat escapes. Adding thermal breaks lowers the u-value and makes the wall resist heat better. Thermal breaks also stop water and moisture problems. They keep parts of the wall apart so heat does not move easily. If you use insulated glass too, thermal breaks help buildings follow energy rules.
Thermal breaks in ACP curtain walls stop heat from moving through aluminum frames. This saves money on heating and cooling. It keeps rooms at the right temperature. Using thermal breaks makes curtain walls work better. It helps people feel comfortable and saves energy. Buildings with thermal breaks use less energy and meet higher standards.
Callout: Using thermal breaks and insulated glass together helps curtain walls get lower u-values and higher r-values.
Comparing ACP to Other Materials
 Concrete Panels
Concrete Panels
Concrete panels are strong and protect buildings well. They do not get damaged by weather easily. But concrete lets heat move through it fast. This means heat can leave the building quickly. ACP panels slow down heat loss because they have layers. Concrete panels are heavy and hard to move. This makes them take longer to install. Workers need more tools and time for concrete. ACP panels are light and easy to put up. This saves time and effort. Concrete panels can crack and fade over time. Fixing them costs more money. ACP panels do not rust or wear out fast. This means you spend less on repairs.
Feature | ACP Panels | Concrete Panels |
|---|---|---|
Weight | Heavy | |
Installation Time | Fast | Slow |
Heat Loss | Low | High |
Maintenance Cost | Low | High |
Thermal Performance | High | Moderate |
Glass and Stone
Glass and stone are used a lot in new buildings. Glass lets sunlight into rooms. But glass does not keep heat inside well. Stone is strong and helps with insulation. But stone is heavy and costs a lot. ACP panels keep more heat inside than glass. This helps save energy. In hot places, stone can keep rooms cooler than ACP. But ACP panels are lighter and cost less than stone. They also insulate better than glass. ACP panels have special cores that help save energy. Designers can use ACP to make buildings look nice.
Tip: ACP panels are tough and keep heat in. They are a good pick for saving energy in curtain walls.
Heat Loss Considerations
Heat loss changes how curtain walls work. ACP panels use insulated cores and air spaces to stop heat from leaving. Concrete, glass, and stone let more heat escape. This can make heating and cooling cost more. ACP panels might cost more at first. But they save money later by lowering energy bills and repair costs. Makers give long warranties for ACP panels. This shows they trust their product. When ACP panels are used with ventilated facades, they work even better. They help control heat loss more. People should think about cost, savings, and how well the wall works when picking materials.
Enhancing Insulation
Thermal Breaks
Thermal breaks are very important for ACP curtain walls. Designers put polyamide or rubber between metal frames. This helps stop heat from moving fast through aluminum. The barrier keeps heat from escaping quickly. Builders can also use steel frames or add more protection. This makes the wall hold heat longer. Tests show steel frames can last over 40 minutes in fire. Thermal breaks help lower u-values. This means less heat leaves the building.
Tip: Using thermal breaks in ACP systems makes rooms more comfortable and saves energy.
Cavity Optimization
Making the space behind ACP panels the right size helps insulation. A good air gap slows down heat moving through the wall. Designers use ventilated cavities to get rid of moisture and extra heat. The best cavity size keeps r-values high and u-values low. If the space is too small, more heat gets out. A deeper gap with good airflow keeps insulation strong and protects the building.
Cavity Depth | Thermal Effect | Moisture Control |
|---|---|---|
Shallow | More heat loss | Poor |
Optimal | Less heat loss | Good |
Deep | Best insulation | Excellent |
Supplemental Insulation
Extra insulation makes ACP curtain walls work better. Builders put mineral wool, rigid foam, or fiberglass behind the panels. These materials make r-values go up and stop heat loss. Extra insulation helps keep room temperatures steady. It is best to seal all joints and use insulation everywhere. This lowers u-values and meets tough energy rules.
Note: Extra insulation works best with ventilated cavities and thermal breaks.
High-Performance Glazing
High-performance glazing makes curtain walls insulate even better. Glass with low-emissivity coatings and double or triple panes blocks more heat. When used with ACP panels, it stops heat bridging and lowers u-values. This keeps rooms comfy and cuts energy bills. Special glass coatings reflect sunlight and help control inside temperatures.
Double or triple glazing stops more heat loss.
Low-emissivity coatings help save energy.
Designers who use thermal breaks, good cavities, extra insulation, and high-performance glazing make curtain walls that save energy and protect people.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability

Impact on Building Performance
Aluminum Composite Panels help buildings save energy. They have two thin aluminum sheets and a polymer core. This makes curtain walls good at stopping heat from moving. The panels help rooms stay the same temperature, even in bad weather. Because of this, heating and cooling systems do not work as hard. This means buildings use less energy and cost less to run.
When builders use ACPs with ventilated façades, they add an air gap. This air gap helps stop heat from moving through the wall. It keeps rooms comfortable inside. Studies show ACPs can lower energy use by up to 30%. These panels also make buildings more comfortable for people inside. They help cut down on repairs and keep buildings working well. ACPs help buildings meet energy rules and support green building goals.
ACPs in green curtain walls give shade and block heat. This helps the wall save energy and makes the air cleaner.
ACP in Sustainable Design
ACPs help make buildings more eco-friendly in many ways. They keep heat out and reflect sunlight, so rooms stay cool. The aluminum in ACPs can be recycled many times. This helps the environment and cuts down on pollution. Many ACPs use special fasteners and clear labels. This makes it easy to take them apart and recycle them later.
ACPs help buildings get green certificates like LEED, BREEAM, and WELL by saving energy and making air cleaner.
Strong coatings help ACPs last 20-30 years, so they do not need to be replaced often.
Light panels are easy to move and put up, which lowers pollution from trucks and makes building faster.
New ACPs use plant-based cores and special coatings to be even greener.
Bak-free ACPs do not have bad chemicals, so the air inside is safer. These panels help buildings win green awards. When designers pick ACPs, they make walls that save energy and keep people comfortable in high-performance buildings.
Aluminum Composite Panels help keep heat inside curtain walls. They use recycled metal, tough coatings, and fire-safe cores. These things help save energy and protect the planet. To make them work best and stop heat from escaping, owners should:
Pick panels with high R-value cores like polyurethane foam.
Make sure all joints are sealed and use tongue-and-groove joints.
Add weather barriers to keep out water.
These tips help builders and designers make buildings that are comfy, save money, and are good for the environment.
FAQ
How does ACP improve thermal insulation in curtain walls?
ACP panels have layers and insulated cores. These parts slow heat from moving. The panels help rooms stay at the same temperature. They also stop energy from being wasted.
Can ACP panels be used with other insulation materials?
Yes. Builders use ACP panels with mineral wool, rigid foam, or fiberglass. Mixing these makes the wall’s r-value higher. It also helps save more energy.
Are ACP panels fire-resistant?
Mineral core ACP panels resist fire better than polyethylene core panels. They follow strict safety rules. These panels help keep buildings safe during fires.
What maintenance do ACP curtain walls require?
ACP curtain walls need cleaning and checking often. Look for broken seals or loose panels. Fixing these keeps insulation working well and makes the system last longer.
Do ACP panels help reduce energy costs?
Yes. ACP panels help lower heating and cooling needs. This means owners pay less for energy. People inside feel more comfortable too.


 Concrete Panels
Concrete Panels