
06 Sep Difference Between ACP and Aluminium Sheets
Table of Contents
The biggest difference between ACP and aluminium sheets is in how they are made and used. ACP stands for Aluminum Composite Panel. It has two thin aluminum sheets with a core that is not aluminum. This makes ACP light and easy to bend. Aluminium sheets are made from solid metal. This gives them more strength. Builders and architects must know the difference. This helps them pick the right material. ACPs are now very popular. They cost less, last long, and are easy to put up. People use them a lot in new buildings.
Key Takeaways
ACP panels have a plastic center between two thin aluminum layers. This makes them light and easy to bend. They are also simple to put in place.
Aluminium sheets are made from solid metal. They are stronger and heavier. They work best for jobs that need to be tough and last a long time.
ACP panels come in many colors and finishes. They look modern and are easy to clean. Aluminium sheets can be shiny or have a coating for different looks.
ACP panels have official fire safety ratings and keep heat in well. Aluminium sheets do not burn easily but do not have special fire tests.
You should pick ACP or aluminium sheets based on price, weight, how long they last, design needs, and how they affect the environment.
What is ACP?
 Structure
Structure
Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) has a special layered build. ACP panels have three main layers. The top layer is aluminum. It makes the panel strong and keeps out bad weather. The middle layer is called the core. It is usually made of polyethylene or a mineral mix. This core lets the panel bend, keeps heat in, and helps stop fires. The bottom layer is also aluminum. It gives support and helps block noise.
Note: Heat and pressure stick the layers together tightly. This keeps the panel strong and long-lasting.
The outside aluminum layer gets a coating like PE, PVDF, or nano-coating. These coatings keep out dirt, fire, and tough weather. Makers test ACP panels for peel strength, hardness, fire safety, and how well they last outside. These tests make sure the panels are safe and good quality.
ACP Panel Structure Table
Layer | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
Top Sheet | Aluminum | Strength, weather protection |
Core | Polyethylene or mineral-filled | Flexibility, insulation, fire resistance |
Bottom Sheet | Aluminum | Structural support, sound insulation |
Uses
Architects and builders use ACP panels in many ways. The most common use is on the outside of buildings. Stores, offices, schools, and hospitals often have ACP panels on their walls. These panels are good for new buildings and for fixing old ones.
Inside, ACP panels cover walls and ceilings. Designers use them for furniture too. This gives a modern look and makes cleaning easy. ACP panels are also used for signs and branding. They come in many colors, finishes, and can have printed designs.
ACP panels last a long time and help stop fires.
They keep buildings safe from weather and save energy.
They do not cost much, so many people use them in new buildings.
ACP panels help make buildings look nice, safe, and work well.
What is an aluminium sheet?
 Structure
Structure
Aluminium sheets are flat metal pieces. They are made from aluminum alloys. Factories roll and press them to make smooth surfaces. The thickness of aluminium sheets can change. Most sheets are thin and light. Industry groups sort aluminium sheets by alloy series. Each series has different main parts and features.
Alloy Series | Main Alloying Elements | Typical Composition Characteristics and Uses |
|---|---|---|
1xxx | Aluminum (99% or higher) | Commercially pure aluminum; excellent corrosion resistance, workability, thermal and electrical conductivity; used in electrical transmission lines and food packaging. |
2xxx | Copper | Heat-treatable; high strength and toughness; lower corrosion resistance; often clad; used in aerospace (e.g., alloy 2024). |
3xxx | Manganese (with some Mg) | Non-heat-treatable; moderate strength and good workability; used in heat exchangers, cooking utensils, beverage cans (e.g., alloy 3003, 3004). |
6xxx | Silicon and Magnesium | Heat-treatable; versatile, formable, weldable; moderate strength and excellent corrosion resistance; used in architectural, structural, marine, and consumer electronics (e.g., alloy 6061). |
7xxx | Zinc (with Magnesium, Cu, Cr) | Heat-treatable; very high strength; used in aerospace and high-performance applications (e.g., alloys 7050, 7075). |
Aluminium sheets are strong and last a long time. Many alloys do not rust and carry heat well. Some sheets have a bumpy surface called chequered sheets. This bumpy part helps stop people from slipping.
Tip: You can cut, bend, and shape aluminium sheets easily. This makes them good for many uses.
Uses
Aluminium sheets are used in many jobs. Chequered sheets are good for floors, stairs, and walkways. The bumpy surface keeps people from slipping. Vehicle bodies, toolboxes, and trailers use aluminium sheets. They are strong and not heavy. Factories and stores use aluminium sheets for walls and covers.
Aluminium coils are long rolled sheets. They are used for roofs, packaging, and HVAC systems. These coils do not rust and last outside for years. Different alloys are picked for different jobs. For example, alloys like 1050 and 1100 are good for food tools and chemical parts. They do not rust easily. Alloys such as 5052 and 5083 are strong and handle heavy loads. They are used in cars and ships. Alloys like 6061 and 6063 are used in building parts and cooling systems.
Sheet metal is also used in special building parts, store displays, and safety rails. Food and medicine companies use aluminium sheets for clean rooms and special boxes. Builders like aluminium sheets because they are easy to shape, last long, and can be changed for many needs.
Aluminium sheets can be used inside or outside.
They are tough and do not break easily.
Many businesses use aluminium sheets for safe and strong buildings.
Difference between ACP and aluminium sheets
Composition
Aluminium sheets are solid metal plates. They are made from pure aluminium or special mixes called alloys. Factories use alloys like AA1100 or AA3003 for these sheets. The thickness is usually between 2 and 4 millimeters. Aluminium sheets are strong and can handle wind well.
Aluminium Composite Panels (ACP) are built differently. ACPs have two thin aluminium layers on the outside. There is a plastic core in the middle. The core is often polyethylene or a fire-safe mineral. This three-layer design makes ACPs light and easy to bend. The main difference starts with how they are made. ACPs use less aluminium, so they cost less and weigh less.
Weight
Weight is important when picking between ACP and aluminium sheets. ACPs are much lighter because of their layered design. The plastic core helps lower the weight.
Material Type | Weight (kg per square meter) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
ACP Sheets | Lightweight due to composite structure | |
Aluminium Sheet (2mm) | Solid aluminium, heavier than ACP | |
Aluminium Sheet (3mm) | ~8.1 | Even heavier, solid metal |
Aluminium sheets are heavier since they are solid metal. This extra weight makes them stronger. But it also makes them harder to move and install.
Durability
Both ACPs and aluminium sheets last a long time. Their durability comes from different things. ACPs have layers that protect against weather and damage. The outside aluminium and special coatings keep ACPs from fading or chipping. With good care, ACPs can last over 20 years.
Aluminium sheets are also very tough. Their solid metal build helps them resist hits and strong winds. Sometimes, they need extra coatings to stop rust in rough places. How long each lasts depends on where they are used and what coatings they have.
ACPs work better than many other building materials outside because they resist weather and have protective coatings.
Flexibility
Flexibility is another big difference. ACPs bend easily and can make many shapes. This is good for creative designs and curved surfaces. The plastic core lets ACPs bend without breaking.
Aluminium sheets are stronger but do not bend as much. They are best for flat or simple shapes. Their strength makes them good for jobs needing extra support.
Designers pick ACPs when they want to make cool shapes or modern building fronts.
Cost
Cost matters when choosing materials. ACPs usually cost less than solid aluminium sheets. They use less aluminium, so the price is lower.
Material Type | Price Range (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
ACP Sheets | |
Aluminium Sheets | 7.7 – 16.5+ |
The price of ACPs changes with thickness, coating, and finish. Aluminium sheets cost more because they use more metal. It also costs more to install aluminium sheets since they are heavier.
Environmental impact
There is also a difference in environmental impact. ACPs use less aluminium, so they save raw materials and lower pollution. Their light weight means less energy is needed to move and install them. ACPs help keep buildings warm or cool, saving energy.
Both ACPs and aluminium sheets can be recycled. Special machines separate the aluminium and plastic in ACPs. Recycling aluminium uses much less energy than making new aluminium. Some ACPs are made with recycled parts and avoid bad chemicals, which is better for the planet.
Recycling and proper disposal help both materials support a circular economy.
Maintenance
Taking care of ACPs and aluminium sheets is different. ACPs are easy to clean with soap and a soft cloth. It is important to check the edges and joints to keep water out. Coatings help ACPs stay looking new.
Aluminium sheets may need more care in tough places. Owners might polish them or add new coatings. Aluminium sheets resist fire and damage well, but they can rust if not protected.
Aspect | ACP Panels | Aluminium Sheets (Solid) |
|---|---|---|
Easy, mild detergents, soft cloths | May need polishing, coating reapplication | |
Damage Resistance | Needs edge sealing, UV protection recommended | Stronger, more fire resistant |
Maintenance Focus | Gentle cleaning, routine inspections | Periodic polishing, coating upkeep |
Applications
Where you use ACPs or aluminium sheets depends on their features. ACPs are common for building fronts, wall covers, and inside designs. Their light weight and flexibility make them great for creative projects. ACPs are also used for signs, furniture, and covering columns.
Aluminium sheets are best for jobs needing strength and toughness. Builders use them for floors, stairs, car bodies, and covers in factories. Aluminium sheets are also used for roofs, packaging, and safety rails.
Application Area | ACP Panels | Aluminium Sheets |
|---|---|---|
✔️ Facades, walls, modern designs | ✔️ Roofs, industrial walls | |
Interior Design | ✔️ Walls, ceilings, partitions | ✔️ Clean rooms, displays |
Signage and Advertising | ✔️ Lightweight, easy to print | ✔️ Durable, long-lasting |
Furniture | ✔️ Modern, sleek look | ✔️ Strong, heavy-duty |
✔️ Lightweight, some use | ✔️ High strength, main material |
Knowing the difference between ACP and aluminium sheets helps builders and designers pick the right one. ACPs are light, flexible, and cost less. Aluminium sheets are strong, last long, and work well in tough places.
Aesthetics
 ACP finishes
ACP finishes
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) come in many finishes. These finishes change how a building looks. Designers can pick from many styles to fit their needs.
High-Gloss Finish: This finish is shiny and smooth. It makes rooms look bright. Stores and showrooms use high-gloss ACP panels. They reflect light and look polished.
Wooden Finish: This finish looks like real wood. It adds warmth and style to rooms. People use it in homes, hotels, and schools. These panels are light and easy to clean.
Metallic Finish: This finish looks modern and sleek. Offices and businesses use metallic ACP panels. The surface does not rust and stays shiny for years.
Sparkle Finish: This finish makes panels sparkle and stand out. Malls and fun places use sparkle ACP panels to get attention.
Solid Color Finish: This finish gives a simple and neat look. Schools and offices use solid color panels for a clean style.
Brush Finish: This finish has texture and hides small marks. Busy places use brush finish because it stays nice even with lots of use.
Each finish makes buildings look better and has good uses. Special finishes help ACP panels last longer and need less care. Wooden finishes look natural but are easier to keep clean than real wood. High-gloss panels change with the light and make rooms lively. Metallic finishes add a fancy look and feel.
Aluminium sheet appearance
Aluminium sheets can look different based on how they are treated. Factories use many ways to change how sheets look and work.
Surface Treatment | Visual Appearance | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
Shiny and smooth finish | Used for products that need a bright look | |
Sanding | Refined, smooth texture | Removes rough spots and impurities |
Metallic and protective look | Adds shine and resists corrosion | |
Matte finish, can be colored | Creates a protective layer and adds color | |
Powder Coating | Slightly rough, durable texture | Eco-friendly and lasts long |
Wet Paint | Smooth, decorative effects | Offers many colors and finishes |
Sublimation | Decorative, wood-effect finish | Combines aluminium strength with design appeal |
Anodising gives sheets a flat look and adds color. Painting and powder coating give many colors and textures. This helps aluminium sheets fit many designs. Polishing makes sheets shiny. Sanding makes them smooth. Chrome plating protects and adds a shiny look. Sublimation can make sheets look like wood. This gives designers more ways to be creative.
Fire resistance
ACP fire performance
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) are tested for fire safety. Makers add special cores to slow down flames. These panels go through many fire tests. The table below shows how ACP panels do in each test:
Standard | Test Subject / Description | Fire Resistance Rating / Result |
|---|---|---|
ASTM E-119 | Fire resistance test for wall partition assemblies | |
NFPA 285 | Façade fire test for exterior non-load bearing wall assemblies with combustible materials | Passed (No flame spread beyond specified limits, temperature control within 1000°F) |
EN 13501-1 | Reaction to fire classification | Classified B-s1,d0 (low smoke, limited flame spread) |
ASTM D1929 | Ignition temperature of plastics | Spontaneous ignition at 452°C, flash ignition at 429°C |
ASTM E84 | Surface burning characteristics | Flame spread index low, smoke developed index ≤ 5 |
BS 476 Part 6 & 7 | Surface spread of flame and flame propagation | Class 0 classification (highest fire safety rating) |
DIN 4102 | Fire test of exterior wall assemblies | Passed FR B1 (fire retardant class B1) |
Mineral-filled cores in ACP panels help stop smoke and flames. Some cores have up to 90% minerals. ACP panels with FR Class B or Class A2 ratings follow strict safety rules. Builders use these panels in tall buildings and busy places where fire safety is very important.
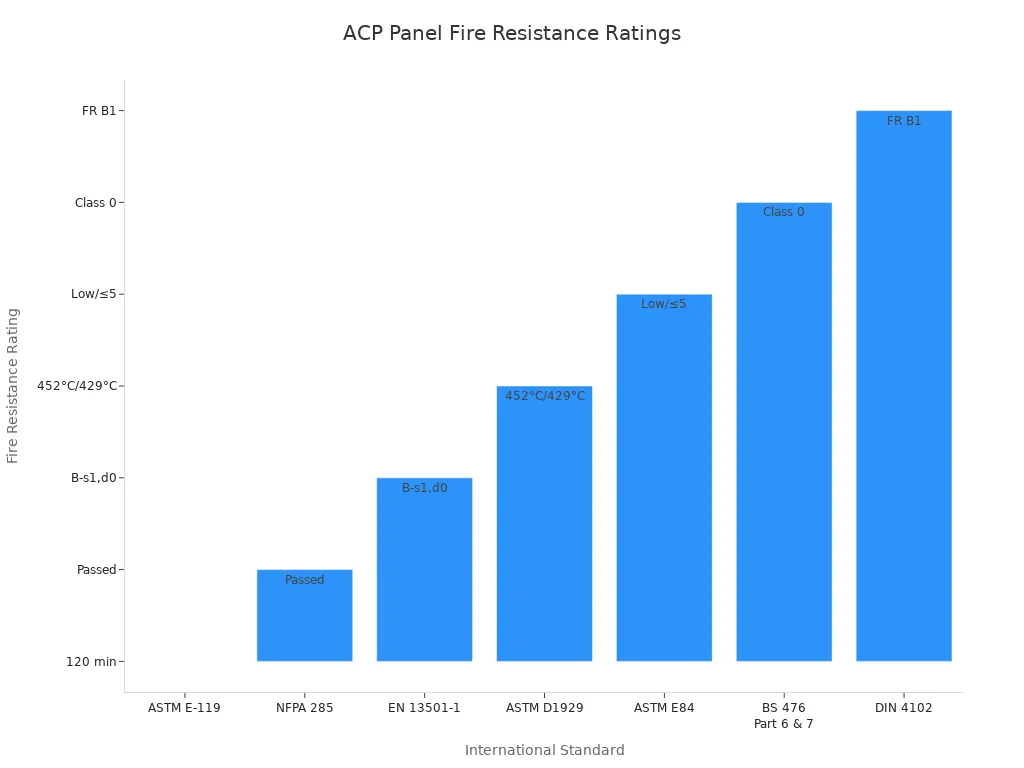
ACP panels stop burning when the fire is gone. They do not let flames spread fast. Their fire safety makes them a good choice for many buildings.
Aluminium sheet fire performance
Aluminium sheets act differently in fires. Solid aluminium does not burn or make harmful smoke. The metal melts only at very high heat, above 660°C (1220°F). Aluminium sheets do not have special fire ratings like ACP panels. Safety groups do not test aluminium sheets for fire resistance in the same way.
Aluminium sheets do not catch fire or help flames grow. They do not go through the same fire tests as ACP panels. Builders use aluminium sheets where materials must not burn. These sheets give basic fire safety because they do not burn, but they do not have extra fire-stopping features like ACP panels.
ACP panels have official fire safety ratings. Aluminium sheets do not have set fire test results. This helps builders pick the best material for each job.
Lifespan
ACP lifespan
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) last a long time in buildings. Most ACP panels on roofs stay good for 30 to 50 years. How long they last depends on a few things. Good installation helps panels fight wind and rain. The weather also matters. Sun, rain, and pollution can slowly damage panels. Cleaning and checking them often keeps them strong and looking nice.
Aluminum does not rust easily, so ACP panels work well outside. Builders pick ACP panels because they handle bad weather. Special coatings like PVDF give more protection. These coatings stop fading and keep panels looking new. Simple advertising ACP panels with basic coatings last about 10 years. Panels with better coatings can last over 15 years with little care.
Tip: Clean panels gently and check for loose edges. This helps ACP panels last longer.
ACP Panel Lifespan Overview
Most panels last 30–50 years on roofs.
Advertising panels with simple coatings last 10 years.
Panels with PVDF coatings last over 15 years.
How long panels last depends on installation, weather, care, and coating.
Aluminium sheet lifespan
Aluminium sheets are strong and last many years. Their solid metal build gives extra toughness. Most aluminium sheets do not rust, even outside. Builders use aluminium sheets for roofs, walls, and floors because they last for a long time.
Aluminium sheets often last more than 40 years. Some stay good for over 50 years. Putting them in the right way and cleaning sometimes keeps them nice. Aluminium sheets do not need much care. Coatings like anodizing or paint make them even stronger. These coatings protect from scratches and bad weather.
Aluminium is a good choice for projects that need strong and lasting materials. Many businesses use aluminium sheets because they stay safe and strong for many years.
Aluminium sheets are a good pick for buildings that need to last a long time.
The difference between ACP and aluminium sheets changes cost, strength, and looks. ACP panels are light and easy to put up. They come in many styles and colors. This makes them good for saving money. Aluminium sheets are stronger and last longer. They do not rust and work well outside or in factories.
When picking materials, teams should think about price, cleaning, the planet, and if the supplier is trusted.
Key Selection Factors:
Think about cleaning and how much care is needed.
Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
ACP Panels | Cheap, many uses | Can fade, needs skilled workers |
Aluminium Sheets | Tough, lasts long, can be recycled | Costs more, can get dents |
Looking at all these points helps teams pick the best material for their project.
FAQ
What is the main difference between ACP and aluminum sheets?
ACP panels have a core made of plastic or minerals. This core sits between two thin aluminum layers. Aluminum sheets are just solid metal. ACP is lighter and bends more easily. Aluminum sheets are stronger and last longer.
Can ACP panels be recycled?
Yes, you can recycle ACP panels. Special machines take apart the aluminum and the core. Recycling cuts down on waste and saves materials. Many companies use recycled parts to make new ACP panels.
Are aluminum sheets better for outdoor use?
Aluminum sheets work well outside. They do not rust and can handle bad weather. Builders use them for roofs, walls, and floors. Coatings help them last even longer.
Which material is easier to install?
ACP panels are easier to put in place. They are light and bend without much effort. Workers can lift and shape them easily. Aluminum sheets are heavier and need more support.
Do ACP panels come in different colors and finishes?
Yes, ACP panels have many colors and finishes. Designers can pick wood, metallic, shiny, or flat looks. This helps match any building style or brand.



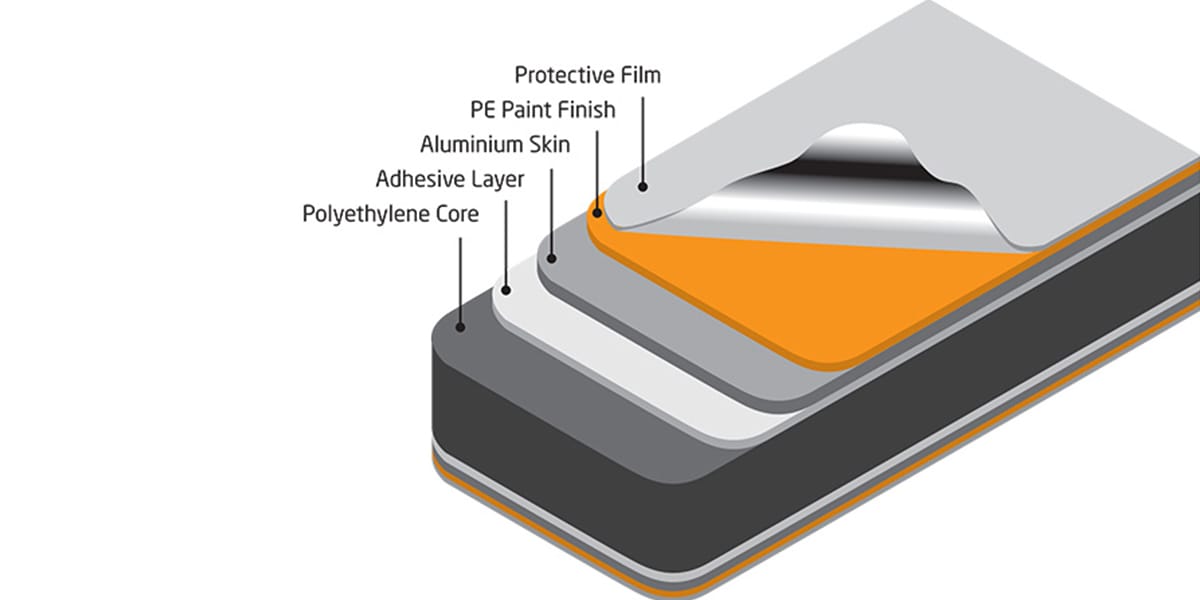 Structure
Structure Structure
Structure ACP finishes
ACP finishes